

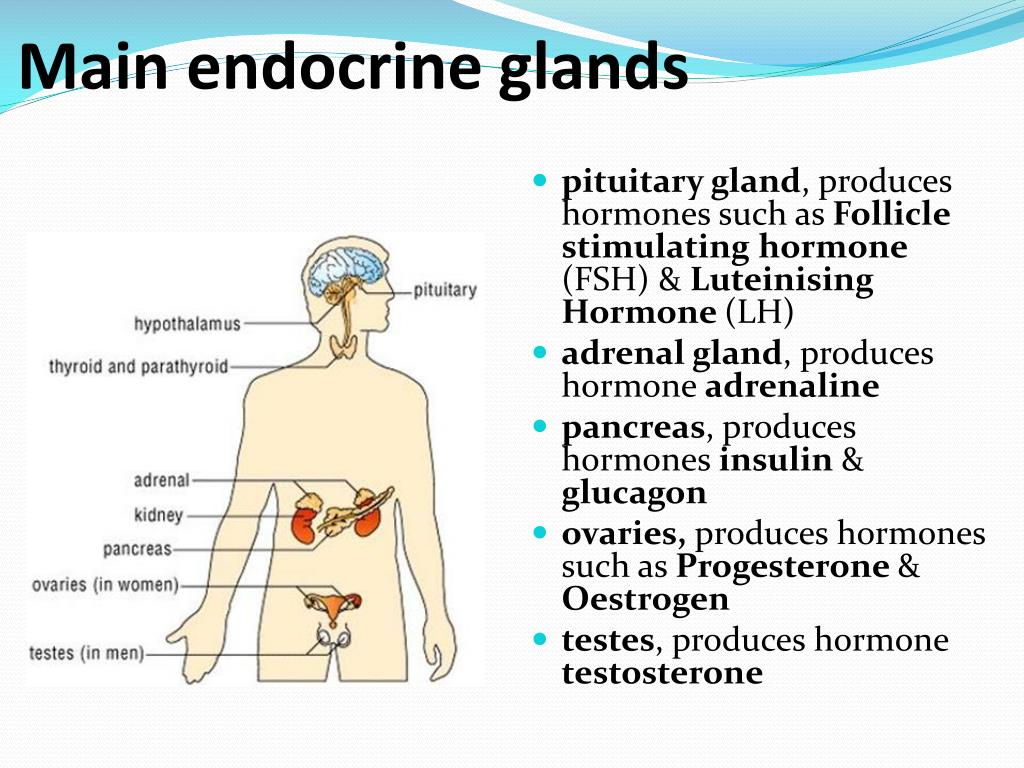
Hypertnsion, Hypokalemia (low levels of K), hypernatremia and Alkalosis. Pathophysiology:Ĭonn ’s Syndrome:Small adenoma’s of the glomerulosa cells results in primary aldosteronism called Conn’s syndrome. Aldosterone increases the activity of several mitochondrial enzymes. Aldosterone produces in response to change in the plasma levels of K and angiotensin-II. Aldosterone increases the number of membrane sodium channels. ATP provides the energy for this active process. The primary action of these hormones is to promote retention of Na + and excretion of K + and H + in the renal tubule. Renin is an enzyme produced in the renal afferent arteriole. This system is involved in the regulation of BP and electrolyte metabolism. Regulation:Īldosterone regulated by Renin, angiotensin system.
But it forms a very weak association with albumin. Secretion:Īldosterone is the most potent mineralocorticoid does not have any specific plasma transport protein. 3 -b-hydroxy steroid dehydrogenase and D5, 4-Isomerasee. For the formation of aldosterone from progesterone are 2 smooth endoplasmic reticulum enzymes. Aldosterone is the most potent hormone in this class. Mineralocorticoids are also 21 carbon steroids. Mineralocorticoids occur in Zona-glomerulosa. Necessry for maintanance of BP and cardiac output disorders of glucocoticoid hormones.Ī ddision’s disease: Primary adrenal insufficiency results in hyperglycemia, extreme sensitivity to insulin, intolerance to stress weighloss, nausea, patients with addision’s disease have low BP.Ĭ ushing’s syndrome: Glucocorticoid excess commonly called Cushing’s syndrome is usually due to pharmacologic use of steroids but may result from an ACTH secreting pituitary adenoma.Suppress the immune response by decreasing the number of circulating Glucosides and the migration of tissue leucocytes.Promote lipolysis but can cause lipogenesis on other sides (Face and trunk) especially higher than physiological levels.Increase glucose production in liver by increasing the delivery of amino acids (Gluconeogenic substrae) from peripheral tissues.Functions: A) Effects on intermediary Metabolism: The secretion of cortisol is dependent on ACTH which in turn regulated by “Corticotropic releasing Hormone”. The main plasma bounding protein is an ”a-globulin” called ”Corticosteroid Binding Globulin”(CBG).

Cortisol circulates in plasma in protein bound and free form. Synthesis:Ĭortisol synthesis requires three hydroxylases that act sequentially on the C17, C21, C11 positions.
A) Cortisol –> Predominant Glucocorticoids in humans, is made in the zona fasiculata.ī) Corticosterone –> less available in humans.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
